Point and Vector
In a game or a 3D graphical application, a point is normally represented by a 4-component column(row) vector.
\(p=\begin{pmatrix}
a\\b\\c\\1\end
{pmatrix}\)
A vector is obtained by subtraction of two points. It has a zero fourth-component,\(\vec{v}=p_{1}-p_{2}=\begin{pmatrix} a\\b\\c\\1\end {pmatrix}-\begin{pmatrix} d\\e\\f\\1\end {pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix} a-d\\b-e\\c-f\\0\end {pmatrix}\)
Matrix
Before start deriving the transformation matrix, it’s important to understand why matrix is preferred in transformation calculation.
Let’s begin the discussion with a simple senario, If we want to rotate a point p with respect to origin o anti-clockwisely 90°
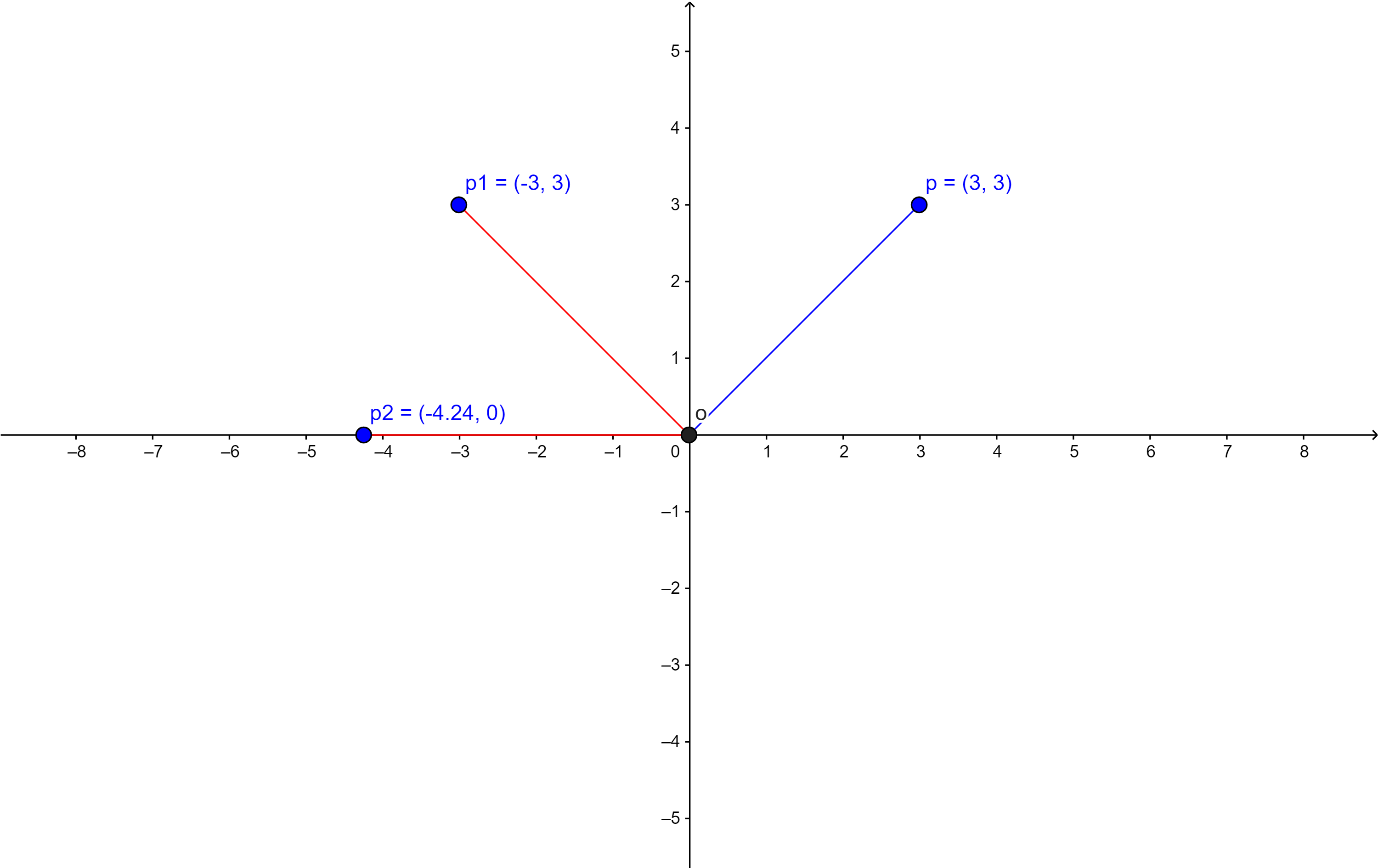
Applying the linear algebra equation Ax=b, it’s easy to write the new postion of p1: \(p_1=M_1 \cdot p= \begin{bmatrix} \cos(90^{\circ})&-\sin(90^{\circ})\\ \sin(90^{\circ})&\cos(90^{\circ})\\ \end{bmatrix}\ \begin{bmatrix} 3\\3\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}-3\\3\end{bmatrix}\) If we rotate p1 to p2 by 45 degree, then it can be writtern as:
\[p_2=M_2 \cdot p_1= \begin{bmatrix} \cos(45^{\circ})&-\sin(45^{\circ})\\ \sin(45^{\circ})&\cos(45^{\circ})\\ \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} -3\\3\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}-4.24\\0.0\end{bmatrix}\]For matrix, the above two steps can be combined into one formula:
\[p=M_2 \cdot M_1 \cdot p_1= \begin{bmatrix} \cos(45^{\circ})&-\sin(45^{\circ})\\ \sin(45^{\circ})&\cos(45^{\circ})\\ \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} \cos(90^{\circ})&-\sin(90^{\circ})\\ \sin(90^{\circ})&\cos(90^{\circ})\\ \end{bmatrix}\ \begin{bmatrix} 3\\3\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}-4.24\\0.0\end{bmatrix}\]Translation
The position of a point can be changed by adding a vector.\(\begin{pmatrix} a\\b\\c\\1\end {pmatrix}+\begin{pmatrix} 1\\2\\3\\0\end {pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix} a+1\\b+2\\c+3\\1+0\end {pmatrix}\)
Rotation
For example,
float rand(float i){
return fract(sin(i)*43758.5453123);
}
float rand2d(vec2 uv){
return fract(sin(dot(uv.xy,vec2(12.123452,78.48254)))*43758.5453123);
}
void mainImage( out vec4 fragColor, in vec2 fragCoord )
{
// Normalized pixel coordinates (from 0 to 1)
vec2 uv = fragCoord/iResolution.xy;
if (uv.y>0.5){
uv*=50.0;
uv.x+=5.0*iTime;
}else{
uv*=75.0;
uv.x-=7.5*iTime;
}
vec2 ipos = floor(uv); // get the integer coords
float random=rand(ipos.x);
if (random<0.4)
random=0.0;
else
random=1.0;
// Time varying pixel color
vec3 col = vec3(random);
// Output to screen
fragColor = vec4(col,1.0);
}
Demo
Notification
Note: This is a notification box.
ome inline Latex: \(a^2 + b^2 = c^2\)
\(\int e^{-kx} \, dx = -\frac{1}{k} e^{-kx}\)
Warning
Warning: This is a warning box.
Error
Error: This is an error box.